
A new development method for flexible electronics
A simple, fast, and green flexible electronics preparation technology was put forward by the research team led by Prof. Zhao Gang from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences to deal with the key constraints of materials and fabrication techniques.
Flexible electronics generally refer to the electronic devices built on conformable or stretchable substrates. In 2000, organic flexible electronics were nominated as one of the Top 10 scientific and technological achievements by Science, together with human genome editing and clone technology. On account of rapid development in the information era, flexible electronics are thought very highly of and have been applied to various fields including electronic skin, human-computer interaction, and implantable medical systems.
As the Internet of Things has stepped into a new stage, multifunctional and highly integrated flexible electronic systems are urgently required to meet more complex application scenarios. Under the challenge of increasingly grim environmental and energy problems, a simple, fast, and green flexible electronics preparation technology was put forward by the research team led by Prof. Zhao Gang from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences to deal with the key constraints of materials and fabrication techniques. This work was published in ACS Nano.
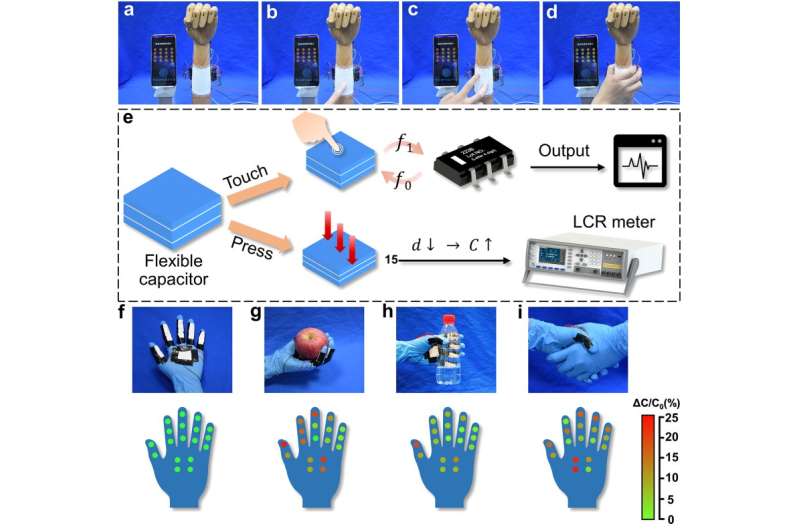
In this work, researchers prepared the thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) membrane by electrospinning, which is used as the substrate, with liquid metal (LM) printed into various patterns on the substrate through premade templates. LM and TPU nanofibers show good interaction during the assembly. This finding is inspiring because scientists have been trying to modify LM or substrate materials to achieve printing and writing of LM since LM is not affinitive with most substrates.
This new system is a typical sandwich structure, which means that the system is built layer by layer and each layer is composed of a TPU membrane and LM printed on it. This strategy invests flexible electronic devices like flexible circuits, resistors, capacitors, inductors, and other devices with excellent stretchability, air permeability, and stability. At the same time, they are reconfigurable.
More future applications were demonstrated in the research, such as flexible displays, sensors, and filters. The new-obtained recyclability and reconfigurability answer the concerns regarding environmental and energetic problems. These findings offer more possibilities in the development and commercialization of flexible electronic devices.
Meng Wang et al, Stencil Printing of Liquid Metal upon Electrospun Nanofibers Enables High-Performance Flexible Electronics, ACS Nano (2021). DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.1c05762
Provided by
University of Science and Technology of China
Citation:
A new development method for flexible electronics (2022, January 7)
retrieved 7 January 2022
from https://techxplore.com/news/2022-01-method-flexible-electronics.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
Stay connected with us on social media platform for instant update click here to join our Twitter, & Facebook
We are now on Telegram. Click here to join our channel (@TechiUpdate) and stay updated with the latest Technology headlines.
For all the latest Technology News Click Here
For the latest news and updates, follow us on Google News.

