Explaining the good and bad cholesterol
Sachin Mittal
Cholesterol is a fatty, waxy substance needed for cell formation and production of various hormones like cortisol, sex hormone, etc, and Vitamin D. It is carried in the blood by protein particles called lipoproteins. Based on the density, these can be LDL (low density lipoprotein), HDL (high density lipoprotein) and VLDL (very low density lipoprotein).
What’s good cholesterol and bad cholesterol
LDL or ‘bad cholesterol’, as it’s popularly known, deposits in the walls of blood vessels, causing their clogging and blockage. HDL or ‘good cholesterol’ transports cholesterol from cells to the liver, lowering the risk of heart disease. Thus, it prevents the clogging phenomenon.
Myths about cholesterol
a) Only obese people can have it: Weight is a factor in high cholesterol risk but even people with normal weight or thin persons can have high cholesterol levels.
b) Since I don’t eat junk/unhealthy food, I can’t have it: While a balanced diet is important for controlling cholesterol, other factors such as heredity, exercise and general metabolic health also play a role.
c) Since there are no symptoms, it does not affect me: High cholesterol is a significant risk factor for cardiovascular diseases and its effects go unnoticed. Regular monitoring, lifestyle choices and aggressive management are crucial for maintaining good health and preventing the risk of stroke, heart attacks, etc.
d) I cannot do anything to change my cholesterol levels: Lifestyle changes and medication (prescribed by doctor) can positively impact cholesterol levels and cardiovascular health. Consistent adjustments in lifestyle can reduce cholesterol levels and lower cardiovascular disease risk.
Certain foods raise cholesterol
Foods, including saturated and trans-fats in animal products, full-fat dairy, fried foods, baked goods and palm oil, can increase cholesterol levels, particularly LDL. While dietary cholesterol is not as dangerous, certain individuals are more sensitive to it. Therefore, those with high cholesterol should eat egg yolks, red meat, fried foods, butter, etc, in moderation. One large yolk contains 210 mg of dietary cholesterol; the recommended total dietary cholesterol intake is 275 mg per day.
Role of diet and exercise
Food and exercise are crucial for lowering high cholesterol levels. Lifestyle changes include avoiding saturated and trans-fats, eating healthy fats, soluble fibre-rich foods and moderate amounts of legumes like chickpeas, peas, beans and lentils. Regular aerobic exercise can raise HDL levels and improve cardiovascular health. Maintaining a healthy weight is also essential for managing cholesterol levels.
Signs and symptoms
High cholesterol is often a silent condition, often unnoticed until it leads to complications like artery narrowing or cardiovascular events (heart attacks, paralysis, stroke) requiring stenting, bypass surgery, etc. Some individuals may have slight cholesterol deposition in the skin, known as Xanthelasma. Regular health check-ups are must and should include lab parameters, considering factors like family history, metabolic health, age, and co-morbidities. Mental health and stress management should also be addressed during annual check-ups to ensure overall well-being.
People who can develop cholesterol and the risks of having a high, uncontrolled cholesterol
Various factors that raise the risk of increased cholesterol levels include age, gender, family history, irregular physical activity, unhealthy diet, obesity, increased alcohol intake and chronic smoking. People with diabetes are more prone to high cholesterol, leading to risk of silent heart attacks and stroke.
Are men more at risk than women?
Women have lower LDL cholesterol levels before menopause, but the gender gap narrows after menopause, as women have an increasing risk of rising LDL levels. Menopausal hormonal changes, particularly a decrease in estrogen levels, may affect lipid profiles, affecting cardiovascular health. High cholesterol risk is caused by genetic and environmental factors, affecting both men and women.
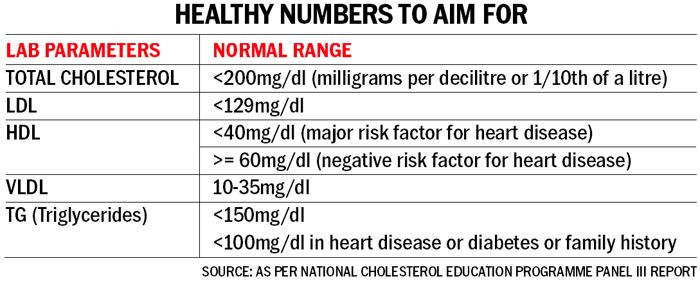
Understanding cholesterol terms
Total cholesterol is the amount of cholesterol in the blood, containing various lipoproteins that transport cholesterol, including LDL and HDL. A low LDL and a high HDL, even if the total cholesterol is within range, suggest a high risk of heart diseases.
VLDL, a type of lipoprotein, transports triglycerides, cholesterol, phospholipids and proteins from the liver to tissues.
Cholesterol ratio compares the amounts of different forms of cholesterol in the blood by dividing the total cholesterol by HDL cholesterol.
Triglycerides, a type of fat, are stored in fat cells and released by hormones for energy between meals. High levels of triglycerides may increase the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Pros and cons of taking statins
Statins are medications that reduce cholesterol production, lowering the risk of heart attack and stroke. They are used in patients with a high risk of these conditions and are protective against future events. Treatment should not be stopped on your own once levels are normalised. While statins are generally well-tolerated, they can have side-effects, such as muscle pains and weakness. Severe muscle-related side-effects are rare. However, the benefits of statins outweigh the adverse effects.
— The writer is an endocrinologist with Fortis, Mohali
Stay connected with us on social media platform for instant update click here to join our Twitter, & Facebook
We are now on Telegram. Click here to join our channel (@TechiUpdate) and stay updated with the latest Technology headlines.
For all the latest Health News Click Here
For the latest news and updates, follow us on Google News.